Custom source
You can extend Botkube functionality by writing custom source plugin. A source allows you to get asynchronous streaming of domain-specific events. For example, streaming Kubernetes or Prometheus events .
Source is a binary that implements the source Protocol Buffers contract.
Goal
This tutorial shows you how to build a custom ticker source that emits an event at a specified interval.
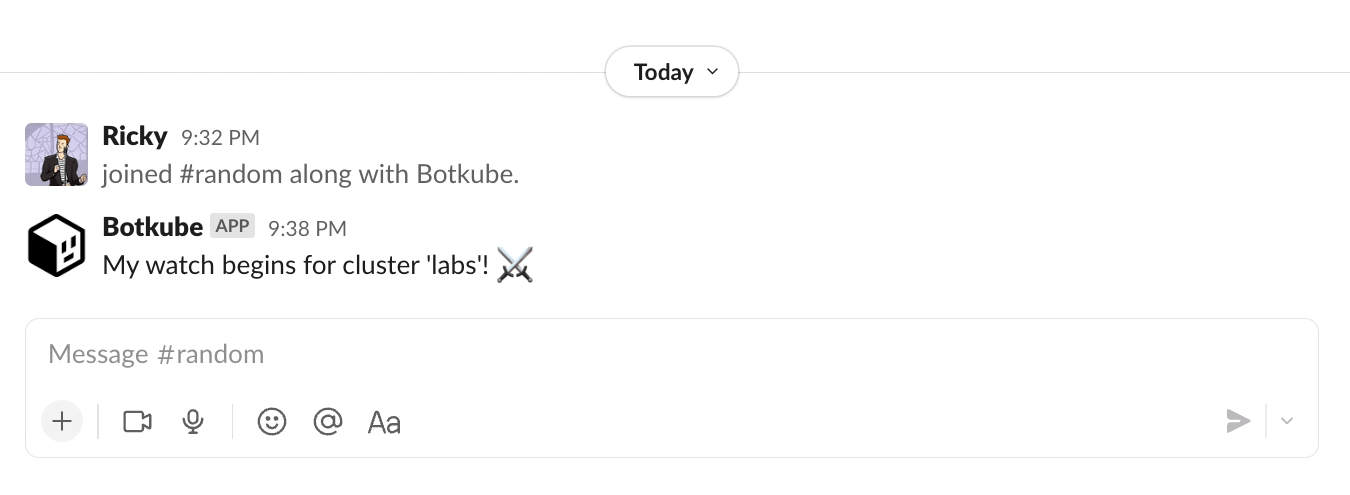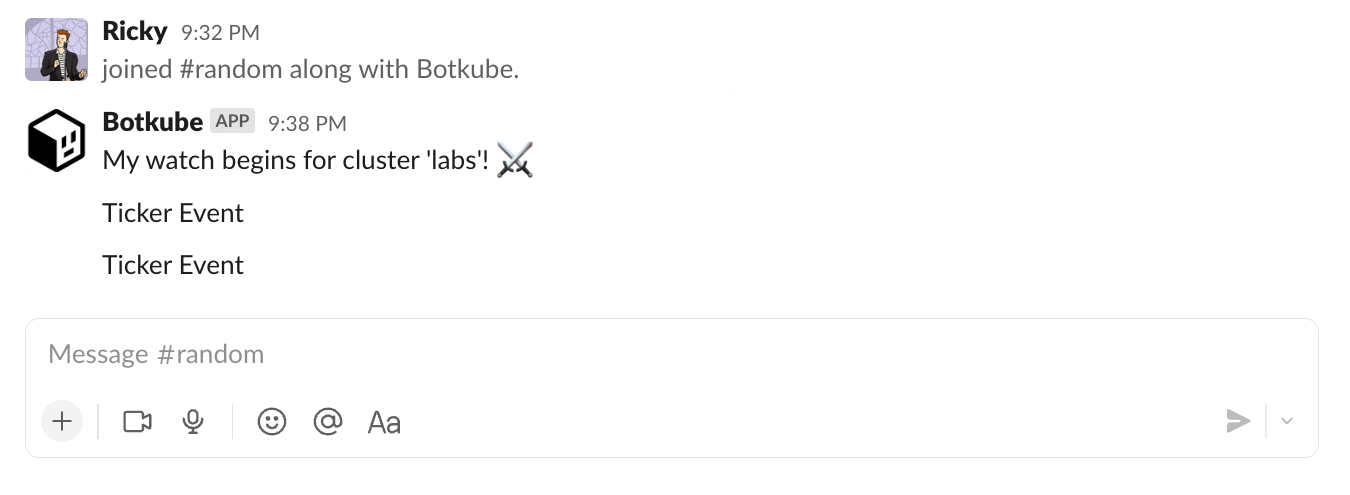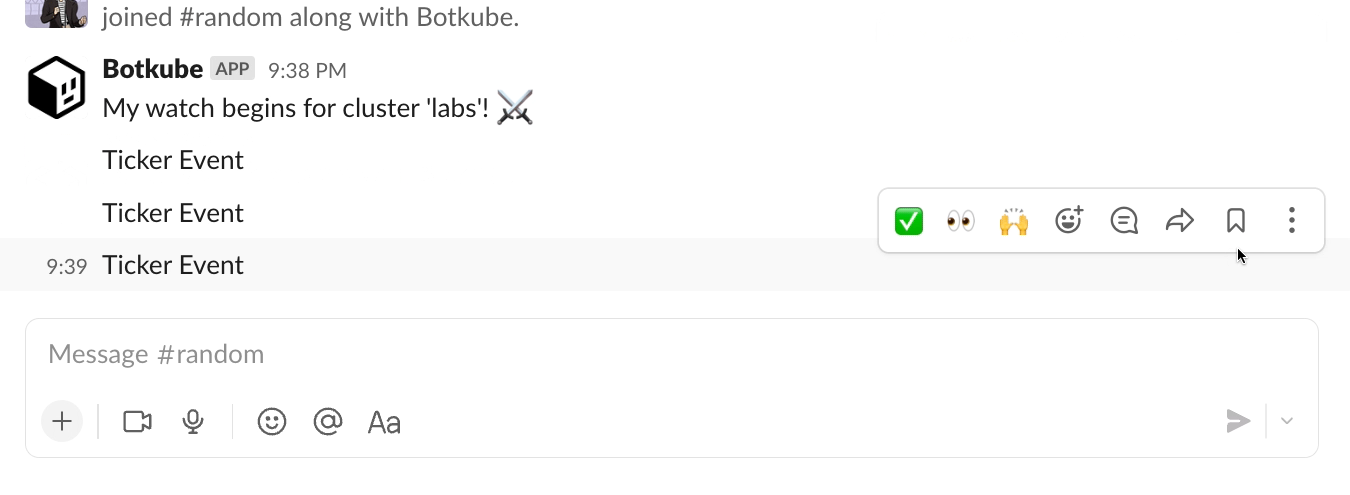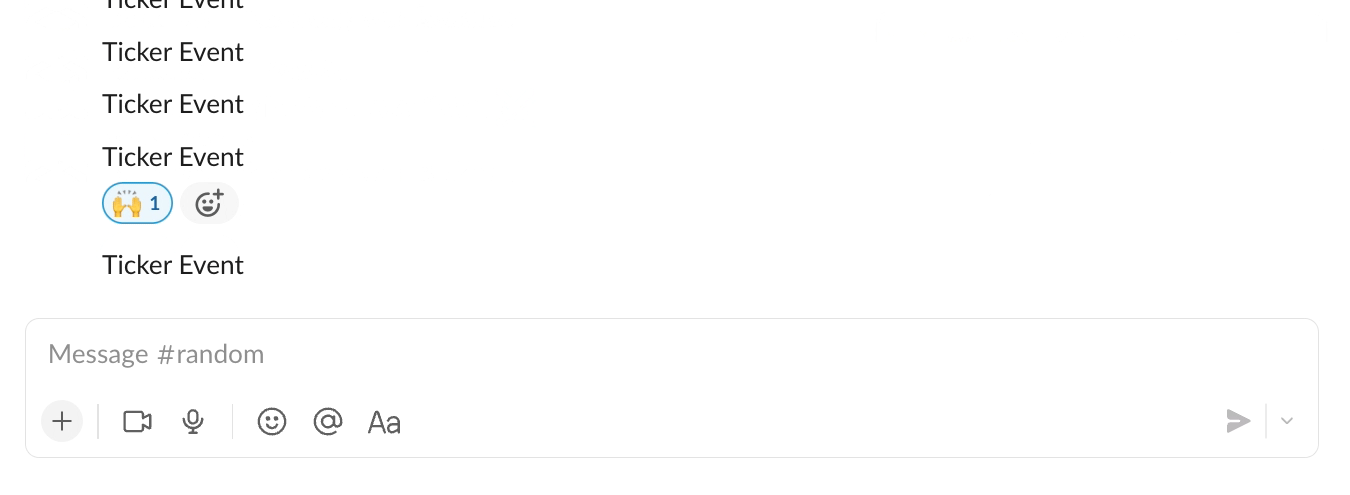
For a final implementation, see the Botkube template repository.
Prerequisites
- Basic understanding of the Go language.
- Go at least 1.18.
- See go.mod for the recommended version used by Botkube team.
- GoReleaser at least 1.13.
Develop plugin business logic
Create a source plugin directory:
mkdir botkube-plugins && cd botkube-pluginsInitialize the Go module:
go mod init botkube-pluginsCreate the
main.gofile for thetickersource with the following template:cat << EOF > main.go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/hashicorp/go-plugin"
"github.com/kubeshop/botkube/pkg/api"
"github.com/kubeshop/botkube/pkg/api/source"
"gopkg.in/yaml.v3"
)
// Config holds executor configuration.
type Config struct {
Interval time.Duration
}
// Ticker implements the Botkube source plugin interface.
type Ticker struct{}
func main() {
source.Serve(map[string]plugin.Plugin{
"ticker": &source.Plugin{
Source: &Ticker{},
},
})
}
EOFThis template code imports required packages and registers
Tickeras the gRPC plugin. At this stage, theTickerservice doesn't implement the required Protocol Buffers contract. We will add the required methods in the next steps.Download imported dependencies:
go mod tidyAdd the required
Metadatamethod:// Metadata returns details about the Ticker plugin.
func (Ticker) Metadata(_ context.Context) (api.MetadataOutput, error) {
return api.MetadataOutput{
Version: "0.1.0",
Description: "Emits an event at a specified interval.",
}, nil
}The
Metadatamethod returns basic information about your plugin. This data is used when the plugin index is generated in an automated way. You will learn more about that in the next steps.Add the required
Streammethod:// Stream sends an event after configured time duration.
func (Ticker) Stream(ctx context.Context, in source.StreamInput) (source.StreamOutput, error) {
cfg, err := mergeConfigs(in.Configs)
if err != nil {
return source.StreamOutput{}, err
}
ticker := time.NewTicker(cfg.Interval)
out := source.StreamOutput{
Output: make(chan []byte),
}
go func() {
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
ticker.Stop()
case <-ticker.C:
out.Output <- []byte("Ticker Event")
}
}
}()
return out, nil
}
// mergeConfigs merges all input configuration. In our case we don't have complex merge strategy,
// the last one that was specified wins :)
func mergeConfigs(configs []*source.Config) (Config, error) {
// default config
finalCfg := Config{
Interval: time.Minute,
}
for _, inputCfg := range configs {
var cfg Config
err := yaml.Unmarshal(inputCfg.RawYAML, &cfg)
if err != nil {
return Config{}, fmt.Errorf("while unmarshalling YAML config: %w", err)
}
if cfg.Interval != 0 {
finalCfg.Interval = cfg.Interval
}
}
return finalCfg, nil
}The
Streammethod is the heart of your source plugin. This method runs your business logic and push events into theout.Outputchannel. Next, the Botkube core sends the event to a given communication platform.The
Streammethod is called only once. Botkube attaches the list of associated configurations. You will learn more about that in the Passing configuration to your plugin section.
Build plugin binaries
Now it's time to build your plugin. For that purpose we will use GoReleaser. It simplifies building Go binaries for different architectures.
Instead of GoReleaser, you can use another tool of your choice. The important thing is to produce the binaries for the architecture of the host platform where Botkube is running.
Create the GoReleaser configuration file:
cat << EOF > .goreleaser.yaml
project_name: botkube-plugins
before:
hooks:
- go mod download
builds:
- id: ticker
binary: source_ticker_{{ .Os }}_{{ .Arch }}
no_unique_dist_dir: true
env:
- CGO_ENABLED=0
goos:
- linux
- darwin
goarch:
- amd64
- arm64
goarm:
- 7
snapshot:
name_template: 'v{{ .Version }}'
EOFBuild the binaries:
goreleaser build --rm-dist --snapshot
Congrats! You just created your first Botkube source plugin! 🎉
Now it's time to test it locally with Botkube. Once you're done testing, see how to distribute it.
Passing configuration to your plugin
Sometimes your executor plugin requires a configuration specified by the end-user. Botkube supports such requirement and provides an option to specify plugin configuration under config. An example Botkube configuration looks like this:
communications:
"default-group":
slack:
channels:
"default":
name: "all-teams"
bindings:
sources:
- ticker-team-a
- ticker-team-b
sources:
"ticker-team-a":
botkube/ticker:
enabled: true
config:
interval: 1s
"ticker-team-b":
botkube/ticker:
enabled: true
config:
interval: 2m
This means that two different botkube/ticker plugin configurations were bound to the all-teams Slack channel. Under source.StreamInput{}.Configs, you will find the list of configurations in the YAML format as specified under the config property for each bound and enabled sources. The order of the configuration is the same as specified under the bindings.sources property. It's up to the plugin author to merge the passed configurations. In this case, the plugin author can override the interval property based on the config order, so ticker-team-b will take precedence as the last item on the list.